A few years back, searching online meant typing something into Google and scrolling through endless blue links until we found an answer. Things look very different today. We can open ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini, ask a question, and within seconds get a clear, human-like response.
These tools can scan millions of web pages in the background, piece together the best information, and present it as if it were written just for you. For decades, businesses played by the old SEO playbook, like using the right keywords, building backlinks, polishing the metadata, and aiming for the top of the search results. In an AI-driven world, that is no longer enough.
The real battle is for visibility inside the AI answer box, where authoritative responses are quoted and cited as trusted sources. Publishing a blog post, launching a product page, or writing a how-to article, the content now has to speak to two audiences: humans and AI models.
Welcome to the era of Generative Engine Optimization, or GEO. In this article, we’ll look at how generative engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity choose what to show, what signals they value, and how you can position your content to be included in these AI-powered answers.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization, or GEO, is all about shaping your content so that AI tools, like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Bing AI, and Perplexity, can easily find it, understand it, and use it when creating answers.
In the past, SEO was mainly about ranking at the top of Google’s results page. The goal was to get clicks on those familiar blue links. GEO works differently. Instead of chasing rankings, the focus is on becoming the trusted source that AI engines pull from when they generate responses.
Here is the big shift. When people use AI assistants, they often get the full answer right there in the chat. They may never need to visit the original website. That means the real win isn’t just showing up in search, it’s being quoted or cited in the AI’s final response.
Success in this new space isn’t measured by clicks. It’s measured by how often your content is read, referenced, and reused by AI.

How Generative Engines Work
To understand Generative Engine Optimization, it helps to know how generative engines themselves actually work. Tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Google Gemini, and Meta’s LLaMA are powered by large language models (LLMs). LLMs are AI systems trained on massive volumes of text to produce human-like text responses.
While these models have extensive pre-trained knowledge, they need up-to-date information and recent trends. For this specific purpose, many LLMs rely on a method called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
RAG enables the model to fetch information from external sources, like websites, articles, PDFs, and databases, in real time and merge it with its internal knowledge before producing an answer. This process boosts accuracy, freshness, and contextual relevance.
Take Perplexity as an example. When it generates a response, it doesn’t just give an answer; it also shows direct links to the sources it used. If your content is clear, well-structured, and trustworthy, it has a better chance of being cited. This is one of the most direct ways to gain visibility in the new search landscape.
Why GEO Matters for Creators and Brands
AI-powered search engines and assistants are becoming the first stop for answers. Whether someone asks Perplexity for product recommendations, ChatGPT to explain a concept, or Google Gemini to summarize a topic, it is the AI tool that decides which sources get surfaced and which get ignored.
For creators and brands, that’s both a challenge and an opportunity. You might have the most valuable insights, but if the AI can’t easily understand your content, find it, or feel confident citing it, your work won’t make it into the conversation.
That’s exactly why Generative Engine Optimization matters. It’s the only way to ensure that the content isn’t just published; it ensures it has a real place in an AI-driven world of instant answers and summaries.
Traditional Ranking ≠ Visibility in AI Answers:
For years, the big SEO win was landing on page one of Google. That top spot meant more clicks, more traffic, more visibility. But things have shifted. With AI Overviews, AI Mode, and conversational tools, a user’s journey often starts and ends right inside the AI’s answer box.
Your content might still technically rank on page one, but if the AI doesn’t pull from it, most people will never see it. In this new search reality, showing up in the answer matters more than showing up in the rankings.
Not Cited by AI = You’re Invisible to Millions
In today’s search landscape, being cited is the new ranking. When someone asks ChatGPT, Gemini, or Perplexity a question, they often get a summarized answer without needing to visit a website. If the content isn’t structured and optimized for these AI models to easily understand, retrieve, and include in their responses, it may not be fully utilized. In that case, we are risking disappearing from the view of millions who now rely on AI-generated answers.
GEO = Long-Term Content Survivability and Discoverability:
Adopting GEO is the future-proofing strategy. As AI continues to integrate into search and everyday platforms, the ability of your content to be consumed, understood, and cited by AI will determine its long-term relevance. By applying GEO principles now, we build assets that remain visible and valuable in the AI-driven search era.
Whether you’re a startup founder, tech writer, or content marketer, GEO gives your content a new life as a source of truth for AI.

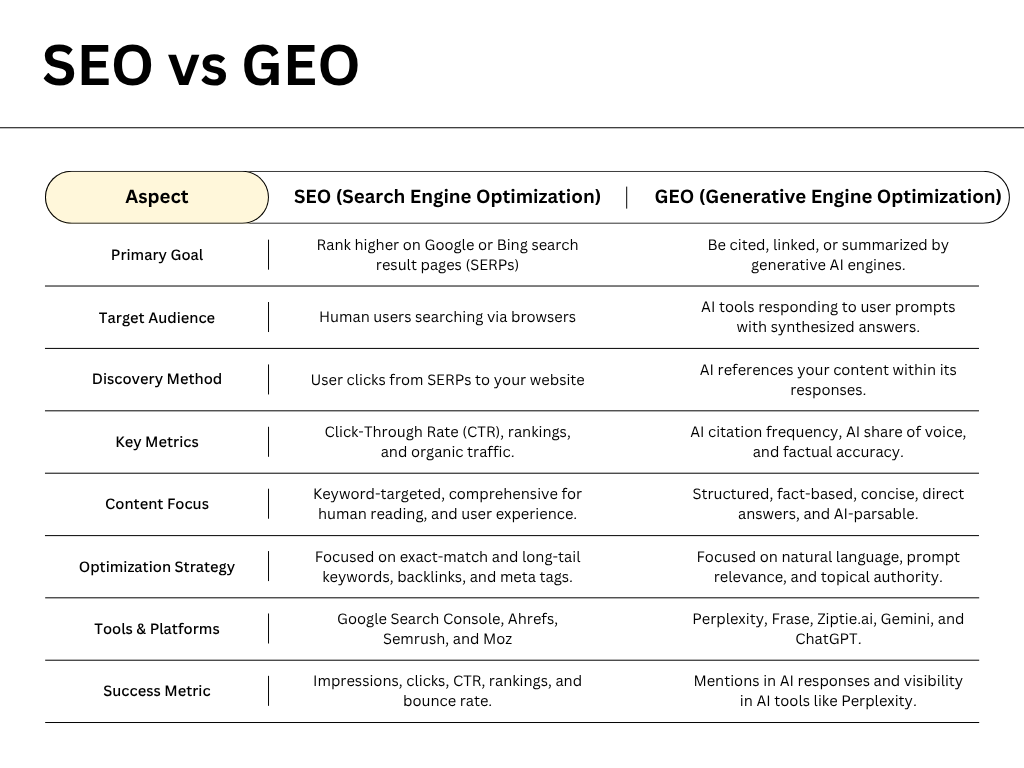
GEO vs SEO: Key Differences
Both SEO and GEO aim to increase visibility and authority, but they differ in how they operate, how users interact with the content, and how success is measured.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) focuses on optimizing websites and content to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). The main objective is simple: drive clicks and traffic to your site.
Generative Engine Optimization involves tailoring your content so that AI models, such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini, can understand, utilize, and cite it within their generated answers. Here, the goal shifts from getting clicks to being included directly in the AI’s response.
How to Optimize Content for Generative Engines
Generative Engine Optimization is about building content that AI can trust, understand, and, ultimately, cite. Let’s break down the key strategies:
Content Quality & E-E-A-T
Large Language Models are designed to prioritize content that feels credible, helpful, and trustworthy. The same old Google’s SEO guidelines E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) apply to generative engines too. Here’s how you can demonstrate E-E-A-T to AI models:
- Experience: Share real-life knowledge, first-hand stories, or practical takeaways from your journey and add layers of credibility that generic content can’t match. Generative engines are increasingly skilled at recognizing this kind of authenticity.
- Expertise: Demonstrate mastery of your subject. Go beyond surface-level explanations, use industry-specific terminology correctly, and provide clear insights. Content that shows genuine depth and subject-matter expertise is far more likely to be trusted and cited by AI models.
- Authoritativeness: Include author bios with credentials, especially in high-stakes fields like health, tech, or finance. Make it clear why the author is qualified to speak on the topic. This builds confidence for both readers and AI systems.
- Trustworthiness: Support your points with credible sources. Link to studies, statistics, research papers, or reputable news articles. This signals factual reliability to both human readers and AI engines.

Use Clear and Structured Formatting
Generative engines don’t “read” your content; they parse it. Content that is clean and has structured formatting makes it easier for LLMs to extract, summarize, and cite. In fact, formatting is one of the simplest ways to improve GEO performance.
- Bulleted lists: Bulleted points work best for features, steps, or comparisons.
- Short paragraphs: Short and crisp paragraphs help answer specific questions concisely.
- FAQ sections: FAQs provide ready-made answers that AI can easily pull into summaries.
Schema Markup isn’t just for Google anymore. AI tools that rely on real-time retrieval are also starting to pick up on structured data. Using formats like FAQ schema, Article schema, or HowTo schema helps both search engines and LLMs quickly understand the purpose and structure of your content.

Semantic SEO & User Intent
Generative Engine Optimization doesn’t rely on simple keyword matching the way traditional search engines do. Instead, it focuses on semantic meaning, context, and related concepts. To gain recognition from these models, the content needs to provide a complete explanation of the topic, supported by relevant subtopics and natural variations.
A big part of this is user intent, the reason behind a search. Every query has a purpose. Sometimes it’s about learning (informational), sometimes it’s about finding a brand or tool (navigational), and other times it’s about taking action, like buying or signing up (transactional). Knowing this helps you decide what kind of content to create and how to structure it so it truly fits the need.
A strong strategy for both traditional SEO and GEO is building topic clusters. This approach involves creating a central pillar page that covers a broad subject and connecting it to multiple supporting articles that explore narrower aspects of the same theme. The interconnected framework strengthens your authority in search engines but also signals to LLMs that the site offers depth, expertise, and reliability on the subject.

Conversational Language & Direct Answers
As generative AI tools become more integrated into the way people search, content that feels conversational is more likely to be cited. Write as if you’re speaking to a curious reader or even directly to a virtual assistant. Instead of using academic or robotic tones, use everyday language that feels natural, helpful, and engaging.
It also helps to structure your content with clear and direct answers. AI engines prioritize responses that get straight to the point, so begin paragraphs with strong summary sentences and then expand with details. This approach makes it easier for models to pull out concise takeaways when generating answers.
Another effective method is using a Q&A style within your content. Anticipate the questions your audience is likely to ask and address them clearly in the body of the article. It makes the content more user-friendly and aligns closely with how LLMs organize, process, and summarize information.
Multimedia Optimization
In addition to textual content, Generative engines can also interpret images, audio, and video content. As models are improving at reading non-text elements, optimizing multimedia content has become an essential part of GEO.
Start with images by adding descriptive alt text that clearly explains what the image represents in context. This helps AI understand the visual content and also connects it to the surrounding text. Make sure that the captions are clear and relevant.
For video content, transcripts are essential. They improve accessibility while also giving AI more textual data to analyze and retrieve. Similarly, for audio or podcasts, short descriptions make the content easier to index and more AI-friendly.
Tools to Monitor GEO Impact
Tracking the success of Generative Engine Optimization is still evolving, but there are a few practical ways to monitor how and where AI tools are referencing your content.
Platforms like Perplexity are a good starting point. You can search for your brand, blog titles, or keywords and check if your content is being cited in their answers. If your URL appears under the Sources tab, it means your content is being pulled into AI responses.
You can also test on Microsoft Copilot or Google Gemini by prompting questions related to your content. Observe if your site or content is mentioned or linked. These experiments provide qualitative insights into how LLMs view and retrieve your material.
While traditional SEO tools like Ahrefs and Google Analytics still play a role in measuring traffic, a new generation of AI SEO tools is emerging. Tools like Frase and Jasper use natural language processing (NLP) to analyze and optimize content based on AI-driven search behavior. Newer platforms like Ziptie.AI and Otterly.AI are specifically designed to track where and how your content is used within generative AI responses.
Though it’s early days for formal GEO tracking, using a mix of these methods can help you spot where your content is gaining traction in this new AI-driven landscape.
Challenges and Limitations of GEO
While Generative Engine Optimization opens up new opportunities for visibility, it also introduces several challenges. Here are some of the challenges in GEO:
- Lack of Transparency in Citations: Generative engines like ChatGPT or Gemini often fail to clearly display the original source of information. Unlike traditional search engines that link directly to websites, GEO outputs typically summarize or paraphrase content without attribution.
- AI Hallucination: Large Language Models are prone to generating inaccurate or fabricated facts. Sometimes, they may merge content from multiple sources or misattribute information.
- Content Parity: A user may receive an answer nearly identical to your blog post directly within the engine, but your site gets no recognition, visits, or conversions. This creates a significant challenge in measuring ROI from content efforts.
- Limited Control: GEO systems often pull from publicly available web data. Unless websites explicitly block AI crawlers with “noai” or other directives, content can be ingested and reused without consent or control over how it appears.

Future Trends: Where GEO Is Going
Generative Engine Optimization is still in its early stages, but it is growing rapidly. One emerging trend is the rise of GEO-focused analytics tools, designed to help brands track how and where their content appears within AI-generated responses.
Search behavior is also fundamentally shifting from the traditional query-to-click model toward a new query-to-answer experience. Users are now getting direct responses without visiting external websites. This fundamental change is likely to pave the way for a new class of AI-first content platforms, optimized not for Google’s algorithms but for visibility within large language models.
Meanwhile, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) is a clear sign that traditional search is blending AI summaries with source links. As a result, this could potentially reduce organic traffic to original sites.
As GEO matures, creators and marketers will need to adapt their strategies to stay visible in a world where answers increasingly come before clicks.

Final Thoughts: GEO as a Competitive Advantage
Generative Engine Optimization isn’t here to replace traditional SEO. Instead, it builds upon it. SEO ensures that the content appears on search engine results pages (SERPs), while GEO makes sure the content is understood, cited, and surfaced by AI. Strong SEO remains the foundation; GEO strengthens it by making your content AI-ready.
The real advantage lies with early adopters. Creators and brands that learn to write for both humans and machines will stand out, earning trust, citations, and visibility in AI-generated answers. In the age of AI-driven search, visibility doesn’t end at SEO; it begins with GEO.
This article was contributed to the Scribe of AI blog by Mehavannen MP.
At Scribe of AI, we spend day in and day out creating content to push traffic to your AI company’s website and educate your audience on all things AI. This is a space for our writers to have a little creative freedom and show off their personalities. If you would like to see what we do during our 9 to 5, please check out our services.
